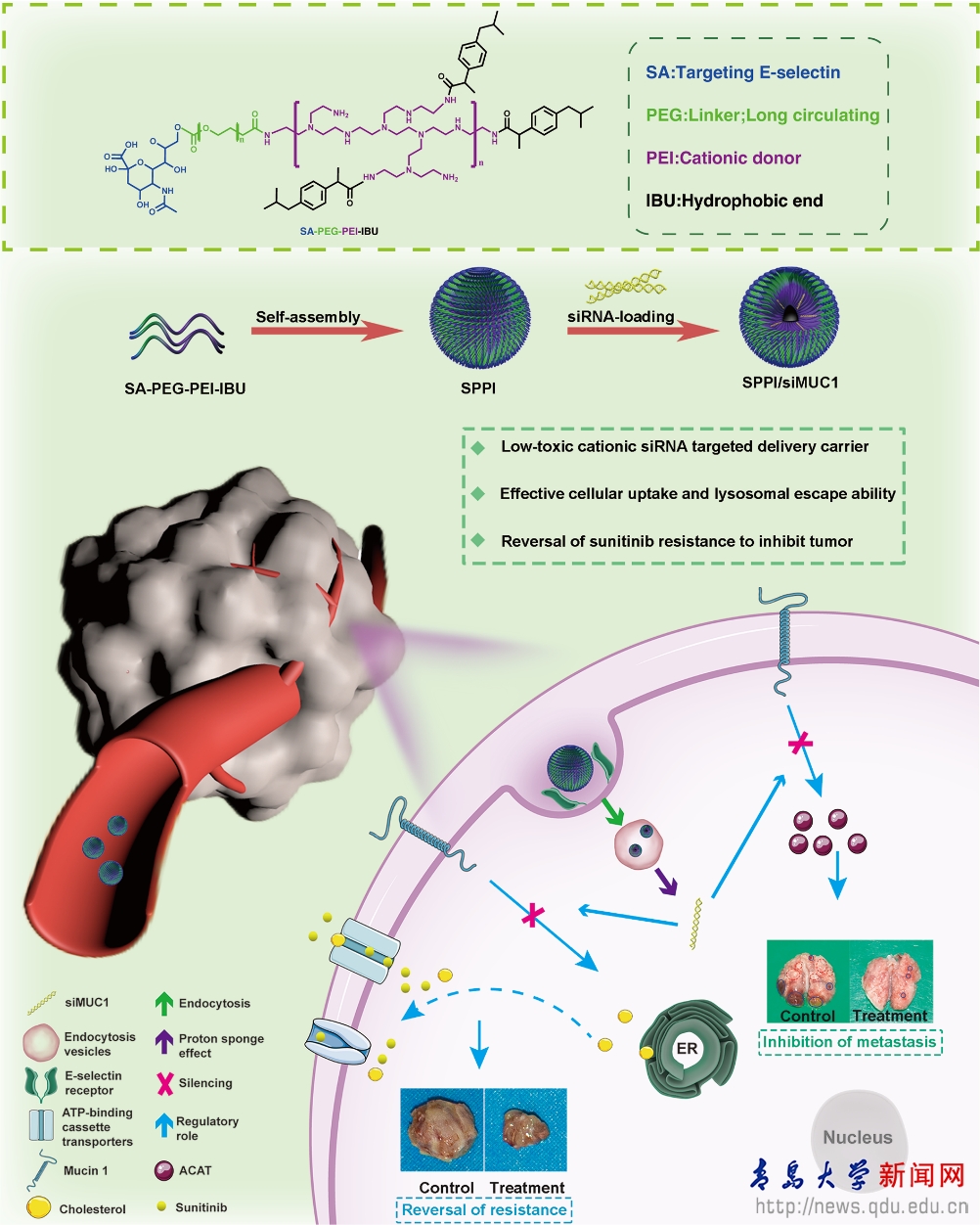
Professor Sun Yong's team from the Department of Pharmaceutics, School of Pharmacy, in collaboration with Chief Physician Zhang Guiming from the Department of Urology at Qingdao University Affiliated Hospital, has made significant progress in the study of tumor-targeted gene drug delivery. Their research, titled "Silencing MUC1 to Regulate Intracellular Lipid Metabolism: Overcoming Sunitinib Resistance and Inhibiting Metastasis in Renal Cell Carcinoma," has been published in the Chemical Engineering Journal (a top-tier journal in the 1st quartile of the Chinese Academy of Sciences journal ranking, IF=13.3). This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation. The first author of the paper is Zeng Xianhu, a 2020 master's student from the School of Pharmacy, and the corresponding authors are Associate Professor Han Shangcong, Professor Sun Yong, and Chief Physician Zhang Guiming.
Tumor cells support their rapid proliferation needs through abnormal lipid metabolism pathways. During this process, Mucin1 (MUC1), a type of transmembrane mucin, has attracted researchers' attention. MUC1 is highly expressed in tumors and is involved in various processes of tumor development, including tumor cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis inhibition, chemoresistance, and metastasis invasion. Recent studies have found that MUC1 also participates in the lipid metabolism process within tumor cells. Its abnormally high expression may promote cholesterol synthesis in tumor cells, and elevated cholesterol levels have become an important factor in inducing tumor cell drug resistance, suggesting a possible link between tumor resistance and lipid metabolism.
Based on the above research background, Sun Yong's team designed and synthesized a polymer SPPI based on sialic acid, polyethylene glycol, polyethyleneimine, and ibuprofen. Using SPPI to deliver siRNA for targeted gene interference in tumor tissues significantly downregulated MUC1 levels in the tumor tissues, strongly inhibiting cholesterol synthesis in lipid metabolism. This further downregulated the expression of multiple resistance-related proteins such as P-GP, ABCG2, and MRP1 associated with cholesterol efflux, reversing the resistance of tumor cells to the chemotherapeutic drug sunitinib. Additionally, it reduced the secretion of inflammatory factors in the tumor microenvironment, inhibiting tumor metastasis.